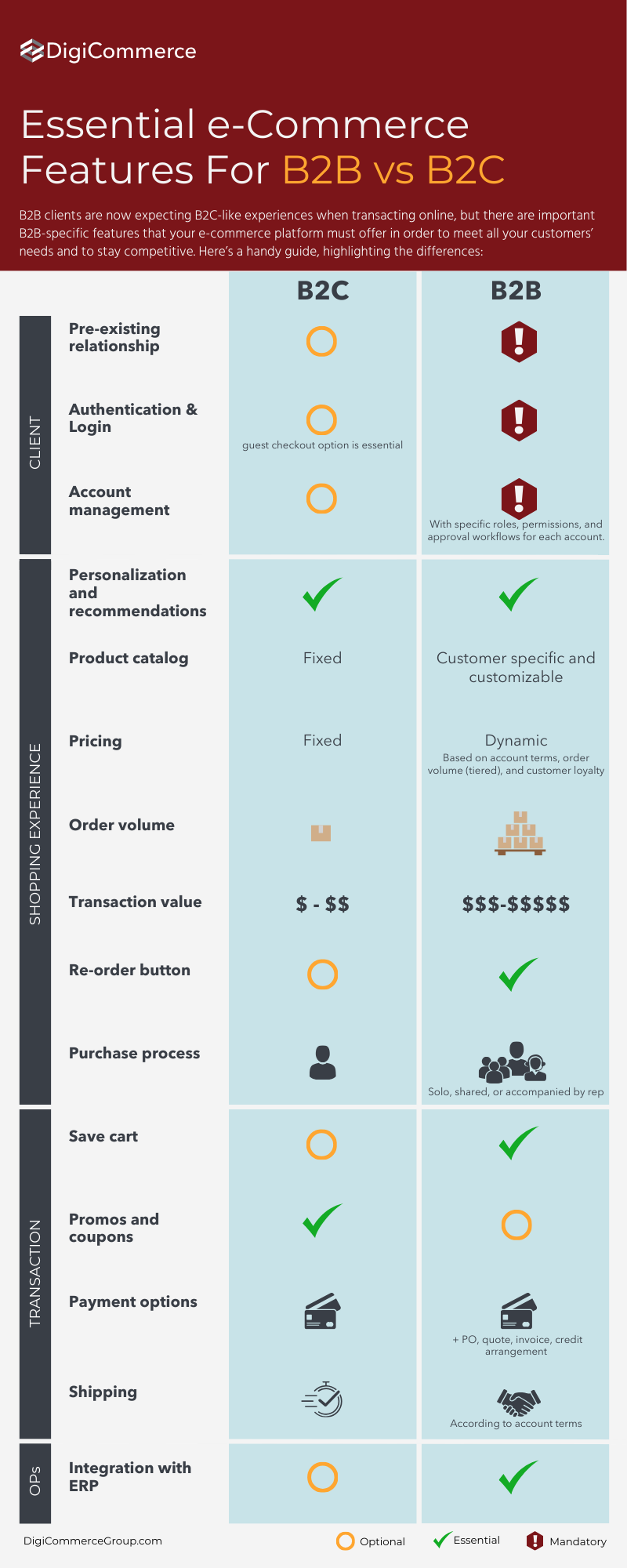
B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-consumer) e-commerce are two distinct models with differences in their target audience, transaction volume, marketing approach, and other key aspects.
Online, B2B clients are now expecting B2C-like experiences when purchasing, but there are important B2B-specific features that your e-commerce platform must offer in order to meet all your customers’ needs and to stay competitive.
Here are the key differences between B2B and B2C e-Commerce:
Target Audience:
B2B: Targets other businesses and enterprises. Transactions involve selling products or services from one business to another.
B2C: Targets individual consumers. Transactions involve selling products or services directly to end-users.
Transaction Volume and Value:
B2B: Typically involves larger transaction volumes and higher order values. Businesses often buy in bulk, and the sales cycles can be longer.
B2C: Generally involves smaller transaction volumes and lower order values. Consumers usually buy individual items or smaller quantities.
Relationships:
B2B: Focuses on building long-term relationships. The sales process often includes negotiations, contracts, and ongoing support.
B2C: Often characterized by shorter, transactional relationships. The focus is on creating a positive buying experience.
Decision-Making Process:
B2B: Involves a complex decision-making process with multiple stakeholders. Purchases are often based on factors such as functionality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
B2C: Decision-making is usually simpler and more individual-centric. Consumers may be influenced by factors like brand image, advertising, and personal preferences.
Marketing and Sales Approach:
B2B: Involves targeted marketing efforts, relationship-building, and often requires customized solutions. Sales may involve negotiation and consultation.
B2C: Utilizes mass marketing strategies, focusing on building brand awareness, attracting a large audience, and creating a positive online shopping experience.
Product Complexity:
B2B: Products or services can be more complex, specialized, and tailored to meet the specific needs of businesses.
B2C: Products are often more standardized and designed for a broader consumer market.
Payment Terms:
B2B: May involve negotiated payment terms, such as net 30 or net 60, and may include invoicing and credit arrangements.
B2C: Transactions typically involve immediate payment through various online payment methods.
E-commerce Platform Features:
B2B: Platforms may include features like bulk ordering, tiered pricing, and account-specific catalogs to cater to the needs of business buyers.
B2C: Focuses on features that enhance the consumer’s shopping experience, such as user-friendly interfaces, product recommendations, and secure payment gateways.
Catering to both B2B and B2C clients
If your company services both B2B and B2C clients, opt for an e-Commerce platform that can cater for both types of clients in one single destination.
As soon as a client logs in, the platform will dynamically display correct store. For example, as a B2B client logs in, the product catalog will be personalized to the types of products they typically have interest in, the prices shown will reflect their negotiated terms, a reorder button will be prominently displayed, and their payment methods will be reflect their account terms. If a B2C client logs in, their store will be adapted to their needs. If a client chooses to remain unauthenticated, they will experience a B2C environment and can shop as a guest.
Ready to launch a B2B commerce experience that is perfectly tailored to your customers needs and your business objectives? Contact us for a free consultation!
In the meantime, save this handy infographic as a reminder of the key B2B features to include in your e-Commerce experience.